Over 2,000 Schools Worldwide Have Adopted the AR Sport “HADO”

The number of schools worldwide that have adopted HADO in education has surpassed a total of 2,000.
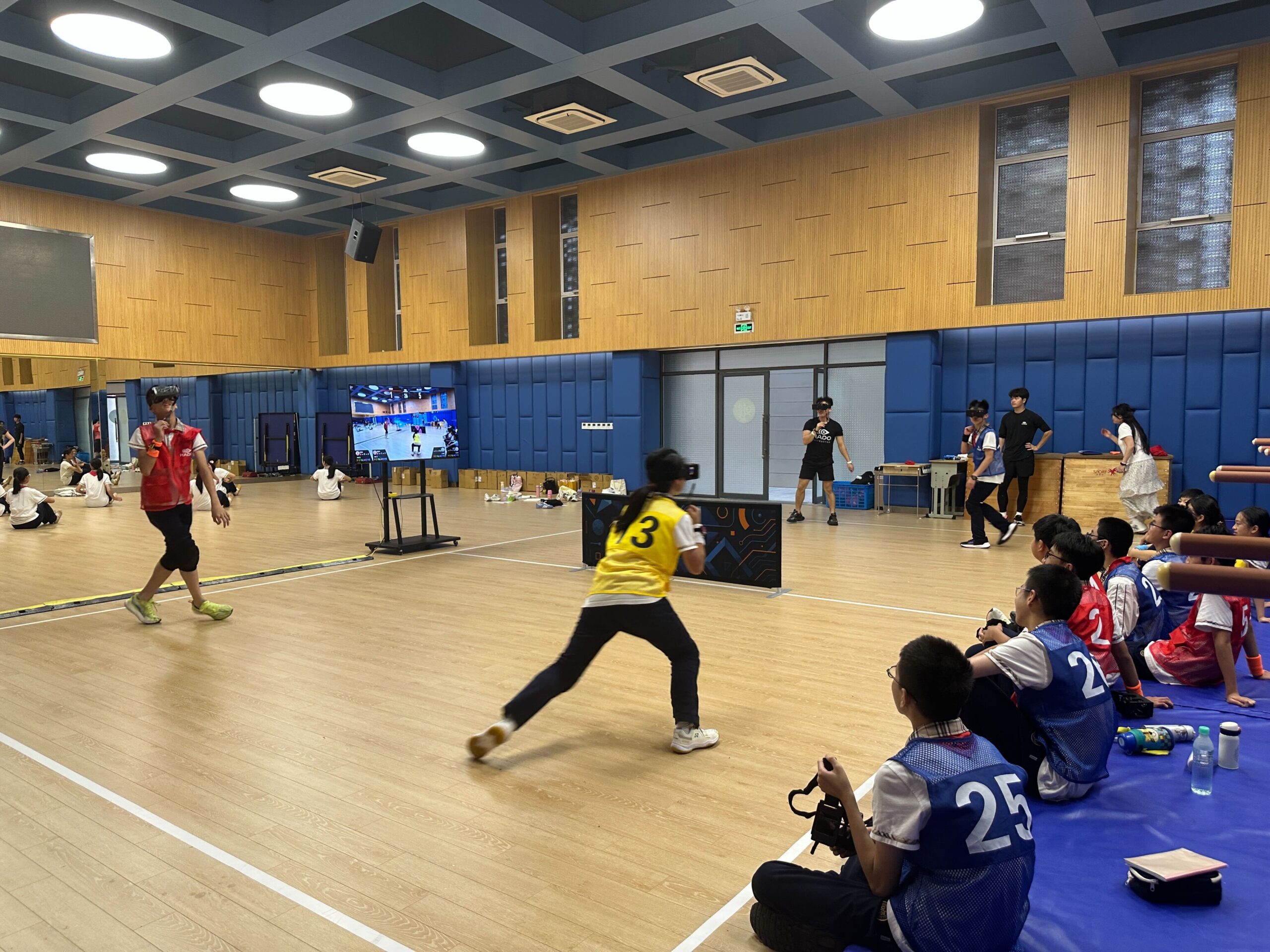
As a new sport utilizing AR (Augmented Reality) technology, HADO is being introduced into physical education and extracurricular activities, while also expanding as an educational program that fosters learning effectiveness and student autonomy.
Why is HADO rapidly spreading in education today?
In today’s classrooms, emphasis is placed on creating environments where diverse students can collaborate and take initiative while experiencing digital technologies firsthand.
At the same time, children’s declining physical activity and “sports disengagement” have become serious issues, making it an important educational theme to provide opportunities where even students who are not athletic can enjoy moving their bodies.
HADO connects these two trends, gaining attention as a new teaching tool that enables both learning and exercise at the same time.
1. Offering equal opportunities for enjoyable physical activity
HADO is designed to be fun regardless of age, gender, physique, or athletic ability. With customizable parameters for energy balls and shields, even students who struggle with sports can participate with confidence, naturally cultivating collaboration and communication skills.
2. Promoting inquiry-based learning through data analysis and critical thinking
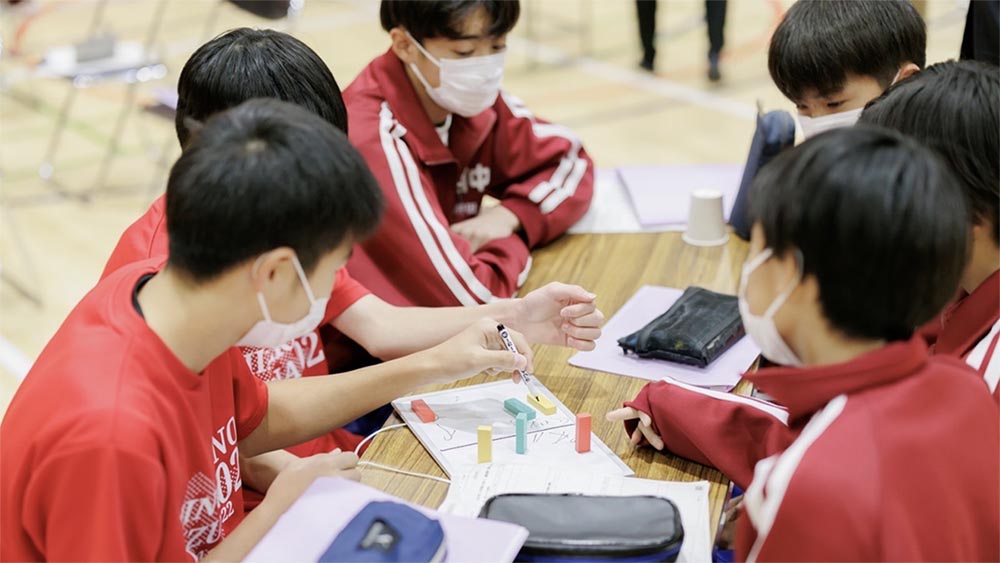
By analyzing match logs that include points, hit rates, and defensive counts, students can actively engage in the hypothesis → verification → improvement cycle, enhancing logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
3. Integrating ICT education to foster intuitive understanding
By interacting with AR and motion tracking through hands-on play, students learn by touching, moving, and thinking—realizing ICT education beyond theory. This approach supports experiential understanding that cannot be gained through lectures alone.
4. Stimulating creativity through development projects
Students can customize elements such as energy balls and field design. This makes HADO adaptable to project-based learning where classes create original content, supporting skills such as planning, collaborative development, and presentation.
In this way, HADO goes beyond “play” or “competition,” becoming a next-generation educational platform that spans physical education, inquiry learning, ICT, and creative development. This is why so many schools are adopting it today.
Case Studies in Japan
In Japan, amid the nationwide GIGA School Program promoting ICT education, more schools are introducing HADO into physical education and inquiry-based learning.
Shizuoka Prefectural Shizuoka Nishi High School
HADO was introduced in PE classes to provide a new form of sports (physical education) that is not bound by athletic ability or gender, serving as a model for inclusive PE.
Yasuda Women’s University
As part of experiential education that nurtures “practical skills,” “problem-solving ability,” and “creativity” required in the digital age, HADO was adopted. It is used to teach human interface design, including understanding AR mechanisms, enhancing body movement, testing UI responsiveness, and designing information display via CG. The university also sees potential for HADO as a tool to deepen programming-oriented thinking.
Honcho Junior High School, Hadano City, Kanagawa Prefecture
HADO was introduced in health and PE classes for “body-building exercises.” Beyond gameplay, it was utilized for inquiry-based learning that nurtures thinking and collaboration through data analysis and strategy meetings. Students also took on the role of instructors, identifying and solving challenges during classes and operations. At community events involving local children and parents, students themselves led as instructors, extending learning into the community.
Case Studies in the United States
The adoption of HADO in education is also accelerating in the U.S. HADO USA has introduced it to over 350 educational institutions, engaging more than 10,000 students, and is conducting outcome assessments in collaboration with STEM and career education programs.
In Palm Beach County, Florida, the “HADO Discovery Program” is implemented in over 100 schools, where students learn teamwork and logical thinking through hands-on experience.
At Iona University in New York, HADO has been officially integrated into the curriculum, simultaneously fostering physical activity and strategic thinking. It has received high praise as an educational value not found in esports.
Comment from Gregory Casiere, Esports Coordinator at Iona University:
“We have created a completely new learning environment where students can simultaneously enhance critical thinking, teamwork, and physical stamina. Unlike traditional esports, HADO encourages students to move their bodies and participate energetically, ensuring that everyone is actively involved. As a result, students have shown remarkable improvements in concentration and collaboration under pressure. This is a highly valuable tool for cultivating ‘life skills’ and essential foundational abilities needed in society. This unique approach has elevated students’ motivation and enthusiasm far beyond my expectations. HADO has brought immeasurable value to both my teaching and student growth.”
Case Study in China
Lansheng Fudan Middle School (Shanghai)
HADO was adopted as an elective after-school course. Every Monday at 3:30 PM, the school holds a 90-minute HADO class. The school is fostering HADO teams and clubs, with plans to participate in school leagues in the future. The introduction reflects the growing demand for diverse elective options that meet students’ varied interests, with HADO emerging as a fresh new choice.